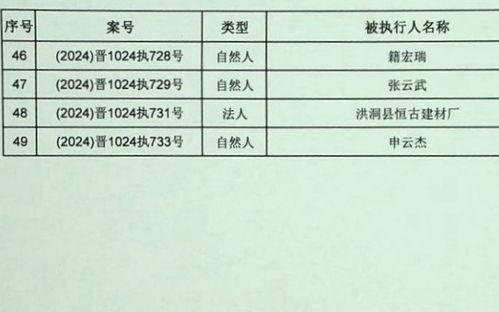
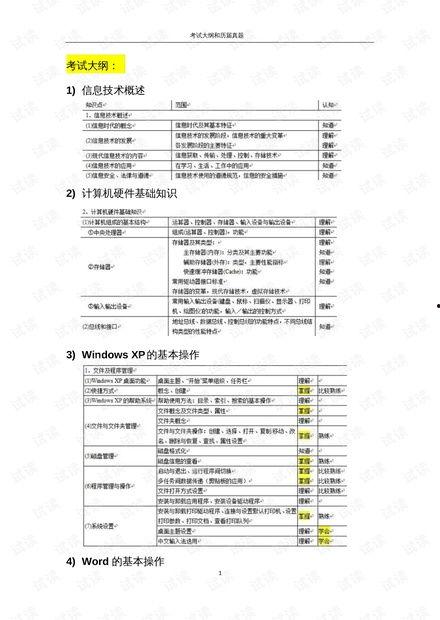
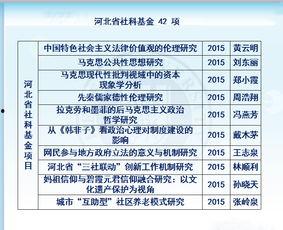
-
大香蕉国产视频在线,揭秘国内影视产业的魅力与挑战
你有没有听说过“大香蕉国产视频在线”?这个词组听起来是不是有点神秘又好奇?别急,今天我就要带你一探究竟,揭开这个话题的神秘面纱。不过,在这之前,我得先提醒你,以下内容可能涉及成人内容,未满18岁的小伙伴们可要绕道而行哦!一、大香蕉国产视频在线:何为“大香蕉...
-
国产区免费,探索国产影视的无限魅力
你有没有发现,最近国产区免费资源好像越来越火了?这不,今天就来给你好好扒一扒这个话题,让你对这个现象有个全面的认识。一、国产区免费资源的兴起你知道吗,国产区免费资源的兴起,其实和互联网的发展有着密不可分的关系。随着网络技术的不断进步,越来越多的人开始关注国...
-
欧美亚洲国产bt,多元文化交融下的影视盛宴
你有没有发现,无论是欧美、亚洲还是国产,电影、电视剧的种子资源在网络上总是那么热门?今天,就让我带你一起探索一下这个神秘的世界,看看欧美、亚洲和国产电影电视剧的种子资源在BT网站上是如何大放异彩的。欧美电影电视剧:经典与时尚的碰撞提起欧美电影电视剧,你可能...
-
国产114
你有没有听说过国产114?这可是个神奇的存在,就像一个无所不知的百宝箱,让你在茫茫互联网中找到你需要的一切。今天,就让我带你一起探索这个神秘的世界,看看国产114到底有多厉害!一、国产114的起源与发展国产114,全称是中国114生活信息查询网,成立于20...
-
日韩国产a,国产A品牌的崛起之路
你知道吗?在时尚界,日韩国产化妆品可是掀起了一股热潮呢!今天,就让我带你一起探索这个神秘的世界,看看这些来自东方的美丽魔法是如何征服全球美妆达人的!日韩国产化妆品的崛起说起日韩国产化妆品,不得不提的就是它们独特的东方美学。从日本的传统和风到韩国的时尚潮流,...
-
国产福利主播,网络新宠,娱乐与公益的完美融合
你有没有发现,最近网上那些国产福利主播可是火得一塌糊涂呢!他们不仅颜值高,才艺多,还特别接地气,让人看了心情都好起来。今天,就让我带你一起走进这个充满活力的世界,看看这些国产福利主播是如何用他们的魅力征服我们的吧!颜值爆表,才艺横溢首先得说,国产福利主播的...
-
国产乱搞
说起国产电影,那可真是让人又爱又恨啊!有时候,那些所谓的“国产佳作”简直让人哭笑不得,仿佛在乱搞电影艺术。今天,就让我带你一起揭开国产电影乱搞的神秘面纱,看看那些让人捧腹大笑、又让人摇头叹息的瞬间吧!一、剧情乱搞,逻辑混乱国产电影中,剧情乱搞的现象可谓是屡...
-
国产老年人性视频,国产老年人性教育视频启示录
你有没有想过,随着科技的发展,老年人的生活质量也在不断提升呢?这不,最近在网上看到一个话题,说的是国产老年人性视频。别误会,这可不是什么不雅的内容,而是关于如何让老年人更好地享受生活,提高性生活质量的话题。下面,就让我带你一起探索这个有趣的话题吧!一、关注...
-
理论国产一级,引领科技创新,铸就民族品牌辉煌
你知道吗?最近在网上看到一个话题,超级有意思的,就是关于国产一级理论的研究。这可不是普通的学术讨论,而是涉及到我们国家科技发展、产业升级的大事儿呢!下面,就让我带你一起探索这个神秘的世界吧!一、国产一级理论的起源与发展说起国产一级理论,那可真是历史悠久。早...
-
国产一道本,传承与创新的文化瑰宝
你有没有发现,最近国产电影界可是热闹非凡呢!尤其是那部《一道本》,简直成了朋友圈的热门话题。今天,就让我带你来全方位解析这部国产佳作,看看它究竟有什么魅力能让众人津津乐道。一、剧情引人入胜,情感真挚动人《一道本》的故事情节跌宕起伏,让人忍不住想要一探究竟。...